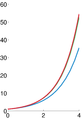
% illustration of numerical integration
% compare the Forward Euler method, which is globally O(h)
% with Midpoint method, which is globally O(h^2)
% and the exact solution
function main()
f = inline ('y', 't', 'y'); % will solve y' = f(t, y)
a=0; b=4; % endpoints of the interval where we will solve the ODE
N = 17; T = linspace(a, b, N); h = T(2)-T(1); % the grid
y0 = 1; % initial condition
% solve the ODE
Y_euler = solve_ODE (N, f, y0, h, T, 1); % Forward Euler method
Y_midpt = solve_ODE (N, f, y0, h, T, 2); % midpoint method
T_highres = a:0.1:b; Y_exact = exp(T_highres);
% prepare the plotting window
lw = 3; % curves linewidth
fs = 20; % font size
figure(1); clf; set(gca, 'fontsize', fs); hold on;
% colors
red=[0.867 0.06 0.14];
blue = [0, 129, 205]/256;
green = [0, 200, 70]/256;
% plot the solutions
plot(T, Y_euler, 'color', blue, 'linewidth', lw)
plot(T, Y_midpt, 'color', green, 'linewidth', lw)
plot(T_highres, Y_exact, 'color', red, 'linewidth', lw)
% axes aspect ratio
pbaspect([1 1.5 1]);
% save to disk
disp(sprintf('Grid size is %0.9g', h))
saveas(gcf, sprintf('Numerical_integration_illustration,_h=%0.2g.eps', h), 'psc2');
function Y = solve_ODE (N, f, y0, h, T, method)
Y = 0*T;
Y(1)=y0;
for i=1:(N-1)
t = T(i); y = Y(i);
if method == 1 % forward Euler method
Y(i+1) = y + h*f(t, y);
elseif method == 2 % explicit one step midpoint method
K = y + 0.5*h*f(t, y);
Y(i+1) = y + h*f(t+h/2, K);
else
disp ('Don`t know this type of method');
return;
end
end